What Is a Title Tag?
A title tag is an HTML element that defines a webpage’s title. When shared, this title is displayed in three primary places: browser tabs, search engine results pages (SERPs), and social media previews. The title tag concisely describes the webpage’s content and helps users and search engines understand what the page is about.
Here’s how a title tag appears in the browser tab, on social media, and in search results:
- Browser Tab: The title tag is shown as the text on the browser tab, allowing users to identify and switch between open tabs easily.
- Social Media: When a link is shared, the title tag often appears as the main headline for that link preview.
- Google Search: In SERPs, the title tag is usually shown as the clickable headline for the webpage. However, Google may rewrite the title if it doesn’t match the search intent or fit the result layout.
Here is an example of what your title tag may look like on Google’s SERP:
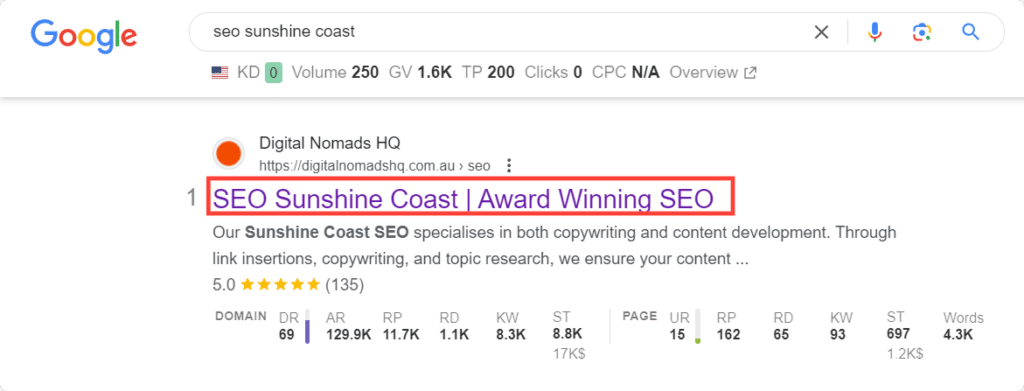
Title Tag Importance
Title tags are important in user experience (UX) and SEO. Here’s why:
- First Impressions: The title is often the first thing users see when browsing search results or social media, influencing their decision to click on the link. A compelling and relevant title tag will improve your click-through rates (CTR).
- Search Engine Ranking: Search engines use the title tag as a signal to understand the content of a webpage, although it’s a minor ranking factor. It can still impact your page’s position in search results when done right.
SEO Best Practices for Title Tags
1. Use Your Primary Keyword
Incorporate your target keyword naturally into the title tag to align with what searchers are looking for. This helps search engines recognise the relevance of your page and can draw in users who see their search terms reflected in your title.
2. Keep It Concise
Aim to keep your title tag under 60 characters. Longer titles can get cut off in search results, so conveying your message within the character limit is important. Tools like Portent’s SERP Preview can help you with this.
3. Make It Unique and Engaging
Every page should have a unique title tag that accurately reflects its content. A well-written title tag should grab attention, create curiosity, and clearly show what the page offers.
4. Differentiating Title Tags from H1 Tags
The title tag and H1 heading do not have to be identical (in fact, it’s recommended for them to be slightly different while conveying the same message). The title tag can be shorter to meet SERP constraints, while the H1 can be more descriptive for users once they land on the page.
FAQs
How Do You Find a Title Tag?
You can find the title tag within the <head> section of a webpage’s HTML. It’s visible in the source code, and some SEO tools can display it as well.
What Is the Recommended Length for a Title Tag?
Keep the title tag between 50 and 60 characters to avoid truncation on search engines. Remember, the exact length can vary based on pixel width, so keep your title concise but impactful.
Is It Compulsory to Have a Title Tag?
While having a title tag on a webpage is not technically compulsory, it is highly recommended. As mentioned, the title tag plays an important role in both SEO and user experience, helping search engines understand the page’s content and providing users with a clear idea of what to expect.
Without a title tag, your webpage may appear less relevant or unprofessional in search results, negatively affecting click-through rates and visibility. Additionally, search engines may generate a title for you, but it might not reflect the content as accurately as a well-crafted title tag.










